Introduction
Biomolecules plays an important role in development, support and reproduction of living organisms. The human body is composed of trillions of cells that performs the essential functions of life. To perform these functions cell takes help from several organic molecules. These organic molecules are known as biomolecules. Biomolecules presenting wide ranges of sizes and structures which involves in various function of life. Biomolecules are classified in four major classes, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids.
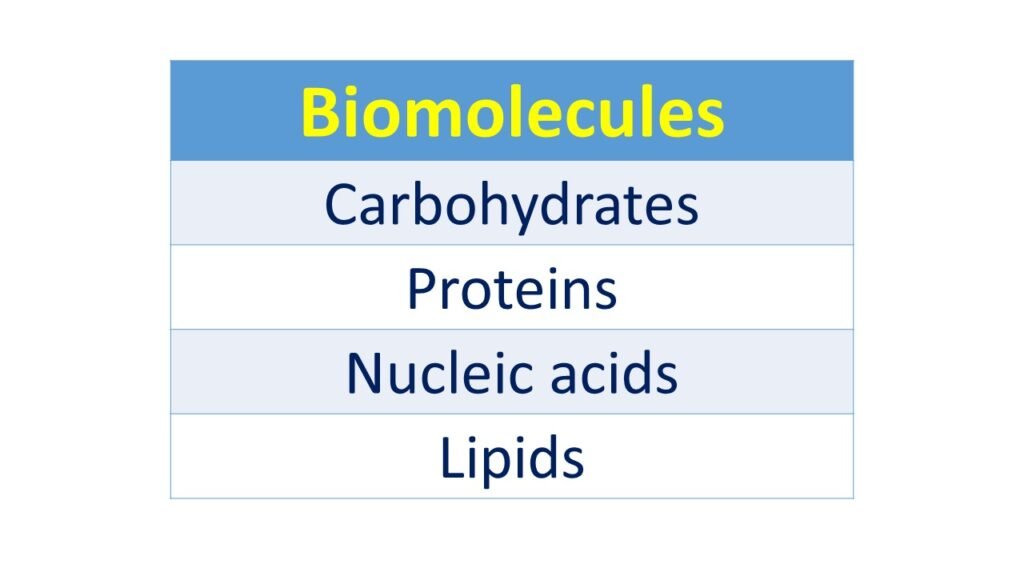
Carbohydrates
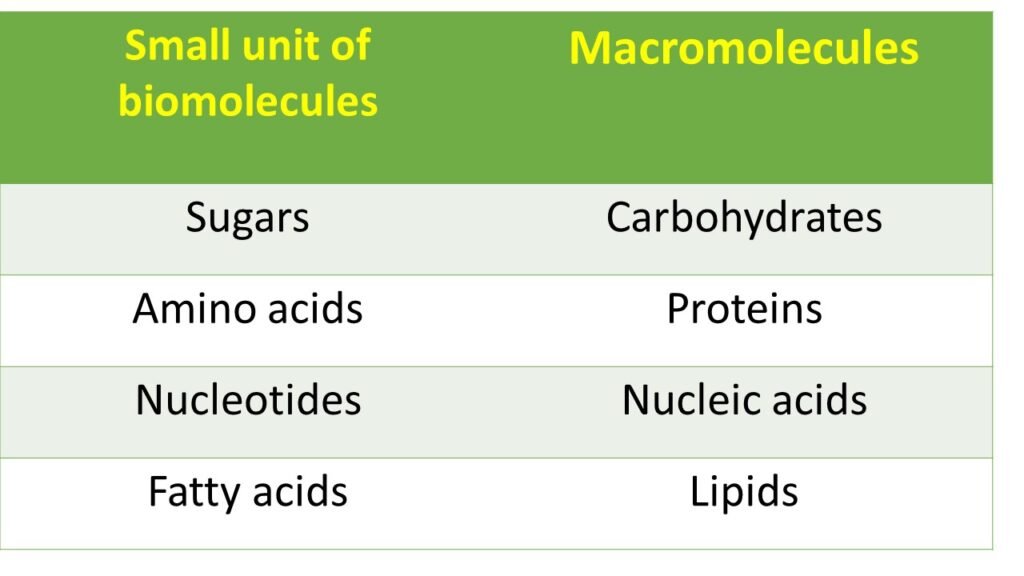
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds derived from their hydrolysis. In simple term we can refer carbohydrates as sugar or a substance which tastes sweet. Carbohydrates are collectively called as saccharides. Saccharides comes from Greek term sakchron means sugar.
Carbohydrates are the main sources of energy. The general formula for carbohydrate is Cn(H2O)n, where n is the number of carbon atoms. carbohydrates are classified on the basis of unit of sugar constituents obtained on hydrolysis. They are classified as monosaccharides (1 unit), disaccharides (2unit), oligosaccharides (3-10 units), polysaccharides (more than 10 units).
Carbohydrates are important constituents of cell structure in the form of glycolipid, glycoproteins, cellular, starch and glycogen. Carbohydrates are basic material for many organic compounds like amino acids, nucleic acids and lipids.
Learn more about Carbohydrates.
Proteins
Proteins are naturally occurring polymers made up of amino acids. These amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds. There are about 22 amino acids which involved in the synthesis of proteins. Proteins make around 50% of cells dry weight.
Proteins are classified in four categories based on their structure as primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure.
Proteins are essential for various vital processes and functions in living organisms. Enzymes, hormones and antibodies are made up of proteins. The proteins which catalysed by chemical reaction are called as enzymes. Proteins which are responsible for protection are called as antibodies.
Learn more about Proteins.
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are the genetic material found in the cell that carries hereditary information from parents to offsprings. Nucleic acids are classified into two types, deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
The monomeric unit of nucleic acid is known as nucleotide and is made up of nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. These nucleotides are linked to each other by a 3’ and 5’ phosphodiester bond. The nitrogen base attached to the pentose sugar makes nucleotide unique and perfect.
There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, adenine (A), guanine(G), cytosine(C) and thymine(T). In RNA thymine is replaced by the uracil (U). The DNA structure is double helix which is formed by hydrogen bonding between two antiparallel polynucleotide chains.
Learn more about Nucleic Acids.
Lipids
Lipids are the organic compounds which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are non-polymeric biomolecules. Lipids majorly involved in membrane structure and chief source of the energy.
Lipids are classified as simple lipids, compound lipids and derived lipids. Some lipid derived substances like vitamins, steroids, prostaglandins are important for therapeutic effect.
Learn more about lipids
Conclusion
Biomolecules are essential molecules for life processes in living organisms. By interacting each other they can make complex living organism from a single cell. The diversity in their size, shape and structure serves diverse roles like catalysing reactions, providing structural support, storing and transfer of genetic information.
Understanding the properties and interactions of biomolecules helps in medicine, biotechnology and other scientific fields.
Frequently asked questions
What are biomolecules?
Biomolecules are an organic molecules, which are essential for life processes.
What are four biomolecules?
There are four types of biomolecules, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids.
What biomolecule is DNA?
DNA is a deoxyribonucleic acid, is a subtype of nucleic acid biomolecule.
What is DNA full form?
Full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid.
What type of biomolecule is ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) comes under nucleic acids category of biomolecules.
What is structure of DNA and RNA?
Structure of DNA is double stranded helix and structure of RNA is single stranded.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us

2 thoughts on “Introduction to Biomolecules”