Introduction
The term pharmacology is derived from two Greek words pharmakon means drug and logos, means science. Pharmacology is the scientific study of the effects of drugs and chemicals on living organisms. It includes study of sources of drugs, their mechanism of action, toxicity, absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drugs. Drugs and their uses are not new to human beings, humans are using various natural resources as a drug to cure the diseases and illness. The most drugs used in ancient civilisations are discovered from the natural resources like plants, animals and minerals. Traditional medicine system has some drawbacks and limitations. The evolution of pharmacology helps to overcome the drawbacks and limitations of traditional medicine system and improves the effectiveness of medicines.
In this article we will see general pharmacology, its branches and general terminologies used in pharmacology.
Branches of pharmacology
There are 15 important branches of pharmacology.
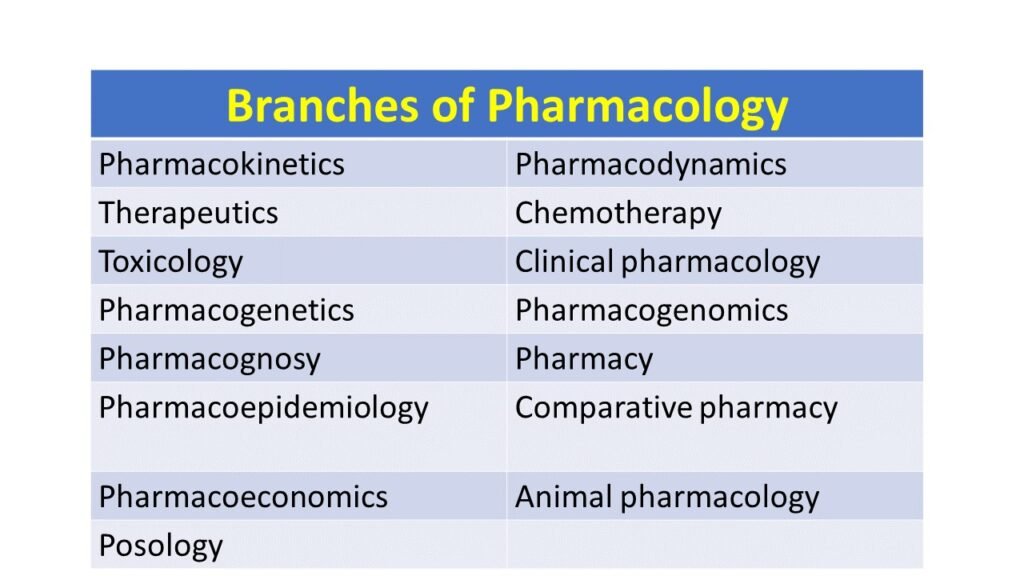
Pharmacodynamics
The word Pharmacodynamics comes from the Greek words pharmakon meaning drug and dynamikos meaning power. Pharmacodynamics is the study of physiological or biological effects of drugs on the body. In simple, pharmacodynamics is nothing but what drug does to the body. Sometimes it is abbreviated as PD.
Pharmacokinetics
The word Pharmacokinetics comes from the Greek words pharmakon meaning drug and kinetikos meaning motion. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how body reacts to the drug. It includes absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drug. Sometimes it is abbreviated as PK.
Therapeutics
Therapeutics is the branch of pharmacology which deals with the science of drugs used for disease treatment. It includes the selection, doses and administration of drugs.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the branch of pharmacology which used the drugs for the treatment of cancer. The medicines used in the chemotherapy works by killing the cancer cell or prevent them to grow.
Toxicology
Toxicology is the branch of pharmacology which deals with the adverse effects of drugs. It is useful to understand the risk of drugs and develop methods to control the drug poisoning.
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology deals with both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics. It is useful to enhance the efficacy of medicine and reduce the adverse effect.
Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of development of new drug from natural resources. It includes identification, isolation and extraction of active compound mainly from plants and other natural resources.
Pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenetics is the branch of pharmacology which studies, how genes affect the action of body on drug. This branch helps to personalise the drug treatment.
Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is the broader application of genomic technology. To develop new drug by further characterizing of old drug. This technology involves artificial joining of DNA of one species to another.
Pharmacoeconomics
This branch of pharmacology deals with the cost of drugs. It includes drug development, manufacturing and marketing.
Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology is the study of drug effects on large population. It includes drug safety, efficacy and utilization on population.
Comparative pharmacology
Comparative pharmacology is the study of the effects of drugs on different species. It mainly focuses on the how different species react to the drugs. It helps to develop new drug.
Animal pharmacology
This is the branch of pharmacology which deals with the study of effects of drug on animals. It helps to develop new safe and effective drugs on human.
Posology
Posology branch deals with the dosage calculations. The word posology derived from two Greek words posos meaning how much and logos means study. Learn more about posology.
Pharmacy
It is the study of the manufacturing formulation and quality control of drug.
General terminologies used in Pharmacology
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical substance that binds to and activates a receptor in the body. An agonist mimics the action of endogenous substances like neurotransmitters or hormones. Based upon their efficacy, agonists are classified in two types; full agonist and partial agonist.
Antagonist
An antagonist is a chemical substance that blocks or inhibits the action of an agonist. Antagonist bind to receptors to prevent a biological response. There are two types of antagonists; competitive antagonists and non-competitive antagonists.
Spare receptor
To produce a biological effect drug needs to bind to receptors in the body. Spare receptors are the receptors which remains unbound after achieving maximal biological response. It means there are more receptors available than the receptors required to produce maximum response.
Addiction
Addiction is a complex condition where a person has a compulsive and uncontrollable desire to use a specific substance, despite knowing the harmful consequences. It may be physical or psychological dependence. Pharmacology helps to study how substances effect the brain reward system that leads to strong behavioral changes in the person.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to a reduced response to a drug overtime, requiring higher doses to achieve the same dosage. In simple it means that the continued use of a drug, the body or brain become less responsive to that drug. Hence higher dose of the drug is required.
Dependence
It is a state of body, where it is adapted to repeated use of drug. This repeated use of drugs increases the tolerance of body to that drug, hence there are chances for addiction. Dependence can be physical, psychological or combination of both.
Tachyphylaxis
Tachyphylaxis is a term to describe, a sudden decrease in the response of body to the drug due to its frequent administration.
Idiosyncrasy
Idiosyncrasy is individual, unique and unusual response to a drug which is not shown in most of the population.
Allergy
Allergy is a hypersensitive immune response to a substance which is typically harmless. The substance which causes allergy called as allergen. Allergy can be adverse drug reaction of some medicines.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
Conclusion
Pharmacology is the science of how drug affects living organisms. The modern pharmacological branches help us to increase the desired effect of medicines and remove the unwanted effects.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us
