Biosensors
Biosensor is a device, probe or electrode consisting of an immobilized enzyme (biocatalyst). It is an analytical device which converts a biological response into an electrical signal. Professor Leland C. Clark is the father of biosensor. He published first example of enzyme electrochemical biosensor by entrapping glucose oxidase in dialysis membrane over a Clark-type oxygen electrode, in 1962. Electrochemical transducers have been combined with enzymes, antibodies and DNA as biochemical recognition components. Nowadays they represent a largest category of biosensors for food, clinical and environmental sensing. In this article we will see biosensors, working of biosensors and applications of biosensors in pharmaceutical industries.
Ideal properties of biosensors
- It should provide accurate, precise and reproducible results.
- It should be free from electrical noise (unwanted disturbance in electrical signal).
- It should be cheap, small, portable and capable of being used by semi-skilled operators.
- The reaction should be independent from physical parameters (like stirring, pH and temperature).
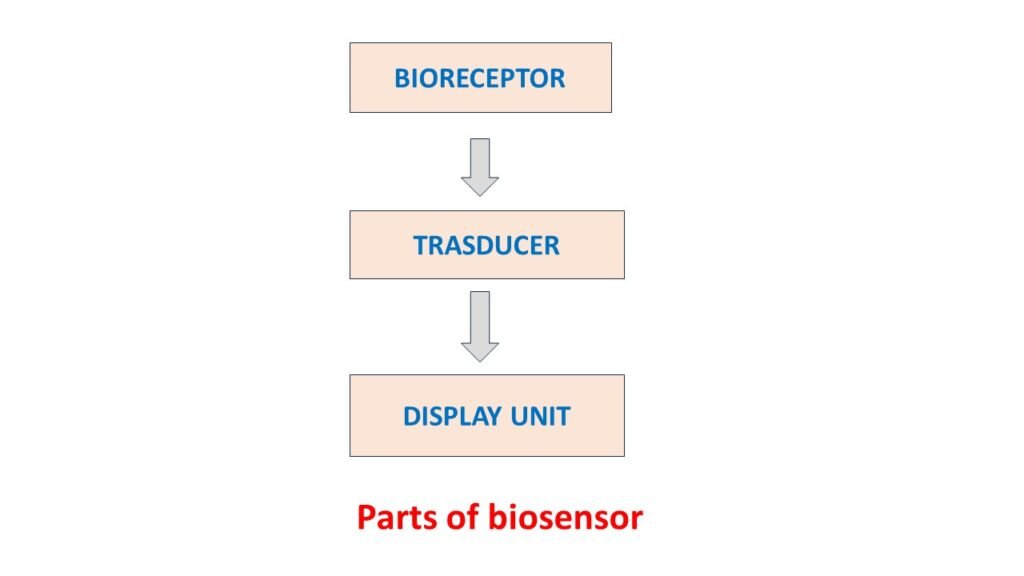
Components of biosensors
Biosensors consists of immobilised enzymes or cells which are used in detection system. There are three main components of biosensors.
- Bioreceptor: The main purpose of bioreceptor is the detection of various substances like, antibody, nucleic acid, plant cells, animal cells, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP), etc.
- Transducers: Transducers convert the interaction between the analyte (substance to be detected) and immobilised enzyme into a measurable signal. The signal can be physical, chemical or electrical. There are various types of transducers used in biosensing devices, as follows;
- Optical: Absorption, fluorescence, interference
- Electrochemical: Potentiometric, amperometric, conductometric
- Electric and magnet: Dielectric and permeating properties, voltage or current.
- Temperature based
- Mass based
- Display unit: The interaction between analyte and immobilised enzyme is displayed in the form of signal, on the display unit.
Working of biosensors
Enzymes are used as bioreceptors in biosensing device. The enzyme used in the biosensor reacts with analyte. This reaction produces a product which is detected by transducer. The signals formed during this process are converted into different measurable forms. Thess signals are displayed on display unit.
Classification of biosensors
Based on type of transducers the biosensors are classified as;
- Electrochemical biosensor
- Amperometric biosensor
- Blood glucose biosensor
- Potentiometric biosensor
- Conductometric biosensor
- Thermometric biosensor
- Optical biosensor
- Fibre optic lactate biosensor
- Piezoelectric biosensor
- Immuno biosensor
Example of biosensors
Glucose biosensor
The target molecule for this biosensor is glucose. The enzyme glucose oxidase is used for the detection of glucose. There is interaction between glucose and glucose oxidase enzymes which leads to formation of gluconic acid. Transducer is of electrochemical type, which detects gluconic acid based on its concentration. The electro chemical signal is measured by amperometer and the current is detected and converted into digital units. Following steps are involved in glucose biosensor working;
- Substrate (Glucose)
- Membrane containing immobilised glucose oxidase
- Product formation (gluconic acid)
- Transducer-electrochemical signal (measured by ameperometer)
- Detector (amperometer)
- Digital display
Penicillinase biosensor
It is used to detect beta-lactam antibiotics in the particular sample. It is also used to determine concentration of antibiotic. Following steps are involved in penicillinase biosensor working;
- Substrate (beta-lactam)
- Detection system (penicillinase enzyme)
- Transducer (pH signal)
- Detector (pH electrode)
- Display unit
Applications of biosensors in pharmaceutical industry
- Early diagnosis of various diseases.
- To detect microorganisms in food, water, etc. for diagnostic purposes.
- To detect microorganism in blood sample or any biological sample for identification of disease.
- Used for detecting chemicals like antibiotics in particular sample.
- Can be used for detecting toxic chemical in nutraceuticals or food supplements, packed foods, etc.
- Used for detection of proteins (biomarkers). These proteins are present in the cancerous organ. Hence used for diagnostic purpose.
Summary
Biosensors are analytical devices used to detect and quantify specific molecules. They play an important role in drug development by facilitating the rapid and sensitive detection of biomolecules involved in drug interactions. They enable real time monitoring of pharmaceutical processes, ensuring product consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. Biosensors are used in detecting proteins, nucleic acids or small molecules.
Frequently asked questions
What is analyte?
The term analyte refers to the specific substance or molecule that the biosensor is designed to detect and measure.
Who is father of biosensors?
Professor Leland C. Clark is the father of biosensor. He published first example of enzyme electrochemical biosensor by entrapping glucose oxidase in dialysis membrane over a Clark-type oxygen electrode, in 1962.
What are three main components of biosensors?
There are three main components of biosensors; bioreceptors, transducers and display unit.
What is the basic principle of biosensor?
The basic principle for biosensor is, ‘the analyte attaches to biological substance forming a bound analyte which generates measurable electrical response.’
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us
