Tideglusib: A Next‑Generation GSK‑3β Inhibitor for Periodontal Regeneration and Bone Healing
Introduction
Tideglusib, a small‑molecule irreversible inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase‑3 beta (GSK‑3β), is widely known for its investigation in neurological disorders. However, over the last decade, this molecule has gained remarkable attention in dentistry, particularly in the fields of periodontal regeneration, alveolar bone repair, and regenerative dental medicine.
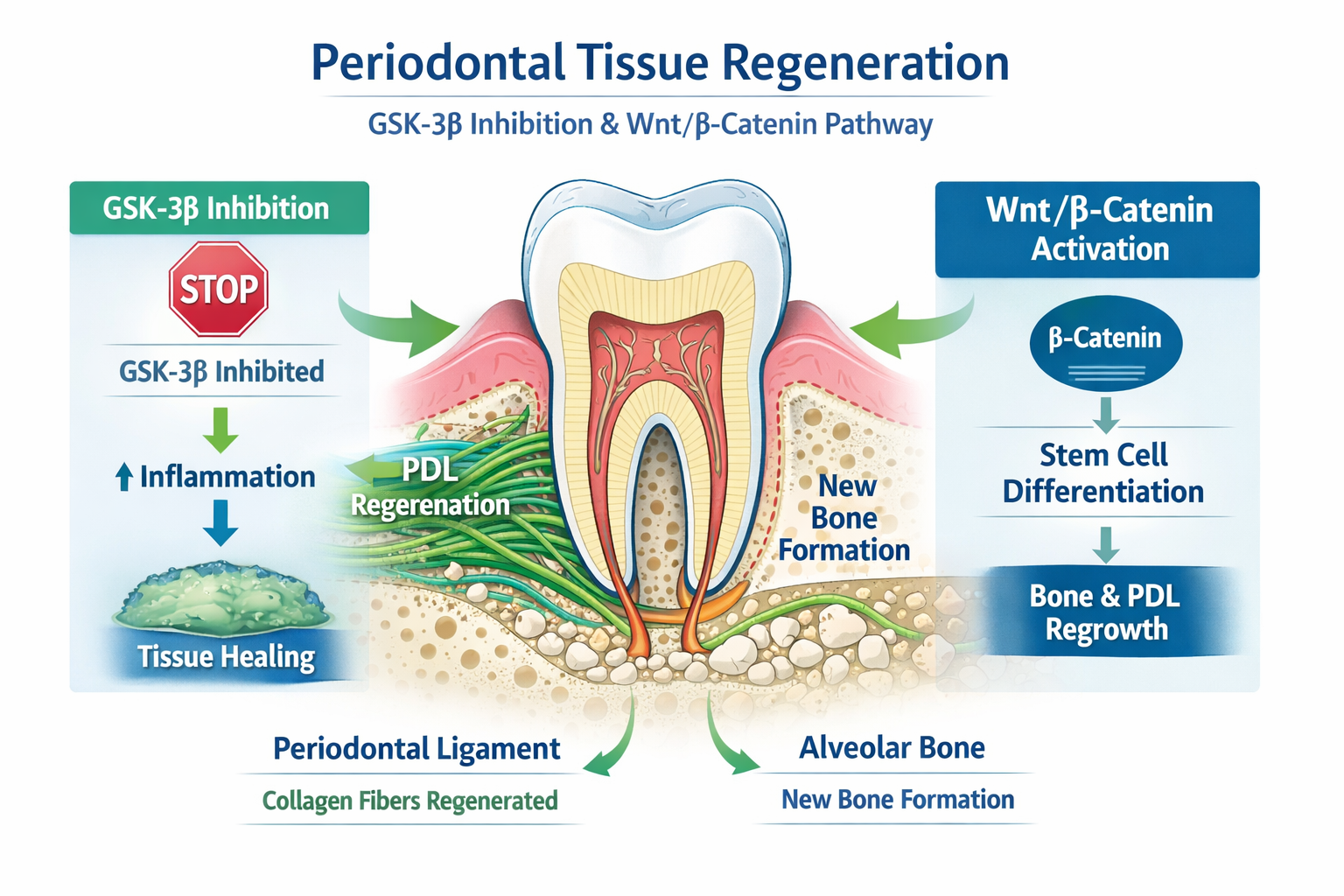
The discovery that GSK‑3β plays a central role in bone formation, stem cell differentiation, and Wnt/β‑catenin signaling has repositioned tideglusib as a potential breakthrough agent in dental tissue regeneration. Unlike conventional dental treatments that rely on mechanical or surgical interventions, tideglusib represents a biologically driven regenerative approach.
Chemical and Molecular Overview
- Generic name: Tideglusib
- Chemical class: Thiadiazolidinone derivative
- Drug type: Small‑molecule kinase inhibitor
- Primary molecular target: Glycogen Synthase Kinase‑3β (GSK‑3β)
- Potential dental routes: Local delivery (gels, scaffolds, microspheres), topical formulations
The molecular structure of tideglusib enables irreversible inhibition of GSK‑3β, a key regulator of osteogenesis and periodontal tissue homeostasis.
Role of GSK‑3β in Oral and Dental Biology
GSK‑3β is a crucial intracellular enzyme expressed in:
- Osteoblasts
- Periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- Dental pulp stem cells
- Alveolar bone tissue
Functions Relevant to Dentistry
- Regulation of osteoblast differentiation
- Control of bone remodeling
- Modulation of inflammatory responses in periodontal disease
- Regulation of Wnt/β‑catenin signaling, essential for tissue regeneration
Pathological Overactivity in Oral Diseases
Overactivation of GSK‑3β contributes to:
- Alveolar bone loss in periodontitis
- Impaired periodontal regeneration
- Delayed bone healing after extractions
- Reduced osseointegration of dental implants
Mechanism of Action of Tideglusib in Dentistry
Tideglusib acts as a non‑ATP competitive, irreversible GSK‑3β inhibitor, leading to activation of regenerative pathways.
Step‑wise Dental Mechanism
- Local or systemic administration of tideglusib
- Irreversible inhibition of GSK‑3β in periodontal and bone cells
- Activation of Wnt/β‑catenin signaling
- Enhanced osteoblast differentiation
- Increased bone matrix deposition
- Promotion of periodontal ligament and alveolar bone regeneration
This mechanism positions tideglusib as a true regenerative dental pharmacological agent.
Applications of Tideglusib in Dentistry
1. Periodontal Regeneration
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that tideglusib:
- Stimulates regeneration of periodontal ligament
- Enhances alveolar bone formation
- Reduces inflammatory bone destruction
This makes it a promising adjunct in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.
2. Alveolar Bone Healing After Tooth Extraction
Tideglusib has shown potential to:
- Accelerate bone healing in extraction sockets
- Reduce post‑extraction bone resorption
- Improve bone quality for future implant placement
3. Dental Implantology
By promoting osteogenesis, tideglusib may:
- Improve osseointegration of implants
- Reduce implant failure rates
- Enhance stability in compromised bone conditions
4. Dental Pulp and Stem Cell Regeneration
Research suggests GSK‑3β inhibition enhances:
- Dental pulp stem cell proliferation
- Differentiation into odontoblast‑like cells
This opens possibilities in vital pulp therapy and regenerative endodontics.
Formulation Strategies for Dental Use
Unlike CNS applications, dentistry favors localized drug delivery, including:
- Biodegradable hydrogels
- Collagen or polymer scaffolds
- Local drug‑eluting membranes
Localized delivery minimizes systemic exposure while maximizing regenerative benefit.
Safety Considerations in Dental Applications
- Local application reduces systemic adverse effects
- No significant cytotoxicity reported in dental cell lines
- Long‑term safety still under investigation
Dental use is expected to have a favorable risk–benefit profile compared to systemic therapy.
Comparison With Conventional Periodontal Therapies
| Aspect | Tideglusib‑Based Regeneration | Conventional Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Biological regeneration | Mechanical/surgical |
| Bone formation | Active stimulation | Limited |
| Long‑term outcome | Potentially durable | Variable |
| Innovation level | High | Traditional |
Current Research Status in Dentistry
- Primarily preclinical and translational research
- Strong interest in periodontal and implant dentistry
- Ongoing exploration of biomaterial‑drug combinations
Future Scope of Tideglusib in Dental Practice
- Chairside regenerative therapies
- Drug‑eluting implant surfaces
- Personalized periodontal regeneration
- Integration with stem‑cell‑based dentistry
Tideglusib represents a shift from repair‑based dentistry to regeneration‑based dentistry.
Conclusion
Tideglusib is emerging as a powerful experimental molecule in regenerative dentistry, with the ability to biologically stimulate periodontal and bone regeneration. By targeting GSK‑3β and activating Wnt/β‑catenin signaling, it offers a novel pharmacological strategy that may redefine future periodontal and implant therapies. While clinical translation is still underway, tideglusib stands at the forefront of next‑generation dental regenerative research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is tideglusib currently used in dental clinics?
No, its dental use is still investigational.
Why is tideglusib important in periodontology?
Because it promotes true bone and periodontal regeneration at a molecular level.
Can tideglusib replace surgical periodontal therapy?
In the future, it may complement or reduce the need for invasive procedures.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us