Top 10 Protein-Rich Vegetarian Foods: Essential Fuel for a Healthy Body
Introduction
Protein is one of the most essential nutrients your body needs daily. While many associate it with meat and eggs, vegetarians can enjoy a variety of high-protein foods that are both nutritious and delicious. From pulses and dairy to seeds and grains, plant-based diets offer ample protein sources that support muscle development, energy production, and overall health.
This article explores the vital functions of protein in the body, lists the top vegetarian protein-rich foods, and offers tips to get the most from your plant-based diet.
🧬 Importance of Protein in the Human Body
Proteins are essential macromolecules that play a fundamental role in the structure, function, and regulation of the human body. They are involved in nearly every biological process and are necessary for the growth, repair, and maintenance of cells and tissues.
🔬 What Are Proteins?
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. The human body uses 20 different amino acids to build proteins, 9 of which are essential—meaning they must be obtained from the diet, as the body cannot synthesize them.
🧠 Importance of Proteins in the Human Body
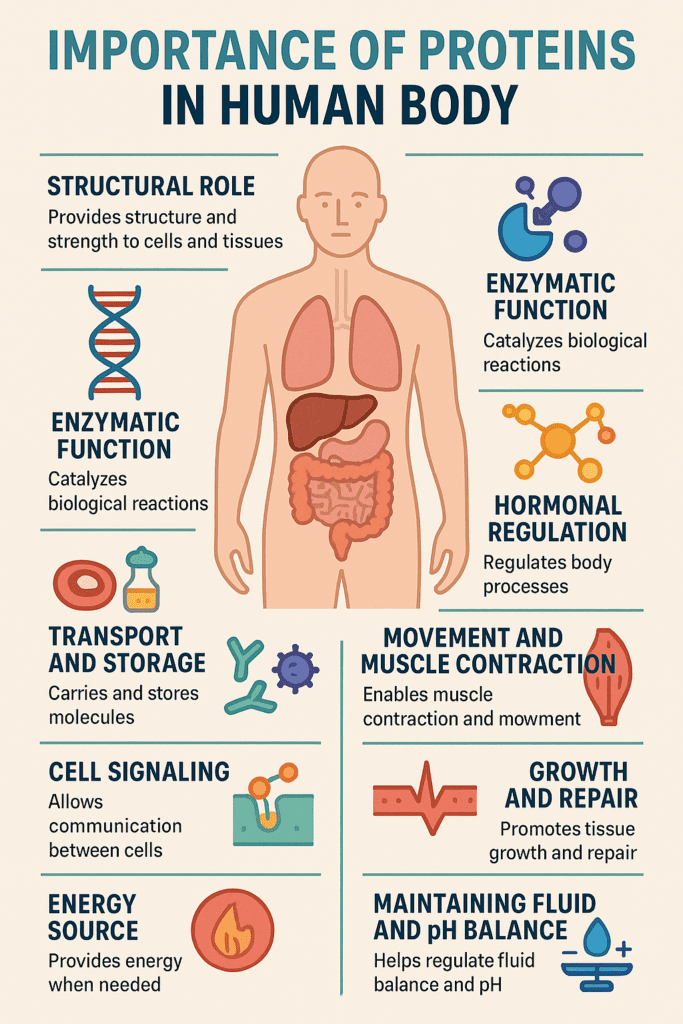
1. Structural Role
Proteins are the building blocks of the body. They provide structure and strength to cells and tissues.
- Examples: Collagen in skin, keratin in hair and nails, elastin in connective tissues.
2. Enzymatic Function
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions that are vital for life.
- Examples: Digestive enzymes like pepsin and amylase help break down food; DNA polymerase aids in DNA replication.
3. Transport and Storage
Proteins help transport various substances throughout the body.
- Examples:
- Hemoglobin transports oxygen in the blood.
- Ferritin stores iron in the liver.
4. Hormonal Regulation
Some proteins function as hormones that regulate body processes.
- Examples:
- Insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
- Growth hormone promotes growth and cell regeneration.
5. Immune Function
Proteins are key players in the immune system.
- Examples:
- Antibodies (immunoglobulins) identify and neutralize pathogens.
- Cytokines help coordinate immune responses.
6. Movement and Muscle Contraction
Proteins are vital for muscle function.
- Examples:
- Actin and myosin are muscle proteins involved in contraction.
- They also help in cellular movements like mitosis and intracellular transport.
7. Cell Signaling
Proteins are involved in communication within and between cells.
- Examples:
- Receptor proteins detect chemical signals like neurotransmitters.
- G-proteins help relay signals from cell surface receptors to internal cellular pathways.
8. Growth and Repair
Protein is critical for tissue growth and repair, particularly important in children, adolescents, pregnant women, and athletes.
- After injury, surgery, or illness, the body requires more protein to rebuild damaged tissues.
9. Energy Source
Although not the primary energy source, proteins can be used for energy when carbohydrates and fats are insufficient.
- 1 gram of protein = 4 calories
However, this is less desirable, as it may lead to muscle breakdown.
10. Maintaining Fluid and pH Balance
Proteins help regulate osmotic pressure and acid-base balance.
- Albumin helps maintain fluid balance between blood vessels and tissues.
- Buffering proteins help regulate blood pH.
⚖️ Recommended Protein Intake
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein:
- Adults: 0.8 grams per kg of body weight per day
- Athletes, elderly, and pregnant women: May need 1.2–2.0 g/kg/day
🧬 Consequences of Protein Deficiency
- Muscle wasting
- Weak immune system
- Edema (swelling)
- Fatty liver
- Poor wound healing
- Stunted growth in children
- Kwashiorkor and Marasmus in severe cases
| Function | Role of Protein |
|---|---|
| Structural | Builds muscles, skin, hair, nails |
| Enzymatic | Catalyzes biological reactions |
| Transport & Storage | Carries oxygen, stores iron |
| Hormonal | Regulates metabolism, growth |
| Immune | Protects against infections |
| Movement | Enables muscle contraction |
| Cell Signaling | Communicates signals inside/outside cell |
| Growth & Repair | Heals wounds, supports development |
| Energy | Provides backup energy |
| Fluid/pH Balance | Maintains homeostasis |
✅ How Much Protein Do You Need?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is:
- 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight for healthy adults.
- Higher for pregnant/lactating women, athletes, and elderly people.
Example: A 60 kg person needs ~48g of protein daily.
🥦 Top 10 Protein-Rich Vegetarian Foods (With Benefits)

1. Lentils (Masoor, Moong, Toor, etc.)
- Protein: 9g per 100g (cooked)
- Rich in: Iron, potassium, fiber, folate
- Bonus: Promotes heart and digestive health
2. Chickpeas (Chana)
- Protein: 8.9g per 100g
- Rich in: Manganese, fiber, B vitamins
- Bonus: Stabilizes blood sugar, aids weight loss
3. Quinoa
- Protein: 8g per cup
- Rich in: All essential amino acids, magnesium, iron
- Bonus: Gluten-free, supports metabolism
4. Paneer (Cottage Cheese)
- Protein: 18g per 100g
- Rich in: Calcium, vitamin B12, fat
- Bonus: Builds bone strength and satiety
5. Tofu & Soy Products
- Protein: 15g per 100g (tofu)
- Rich in: Isoflavones, iron, complete protein
- Bonus: Balances hormones, supports heart health
6. Green Peas
- Protein: 5g per 100g
- Rich in: Vitamins A, C, K, and fiber
- Bonus: Improves digestion and eye health
7. Almonds
- Protein: 21g per 100g
- Rich in: Vitamin E, magnesium, healthy fats
- Bonus: Supports brain function and cholesterol control
8. Chia Seeds
- Protein: 5g per 2 tablespoons
- Rich in: Omega-3, fiber, calcium
- Bonus: Reduces inflammation, supports digestion
9. Greek Yogurt
- Protein: 10g per 100g
- Rich in: Probiotics, calcium, B12
- Bonus: Aids gut health and boosts immunity
10. Amaranth (Rajgira)
- Protein: 9g per cup
- Rich in: Iron, calcium, manganese
- Bonus: Good for bone health and gluten-free diets
🥗 Bonus Tips for Better Protein Utilization
- Pair wisely: Combine cereals + pulses (like rice + dal, chapati + rajma) to form a complete amino acid profile.
- Vitamin C is key: Include citrus fruits to enhance iron absorption from plant-based proteins.
- Soak and sprout: Soaking legumes and seeds reduces anti-nutrients and increases bioavailability.
🤔 FAQs on Vegetarian Protein-Rich Foods
1. Can vegetarians get enough protein without supplements?
Yes. A varied vegetarian diet with legumes, dairy, nuts, and seeds can meet daily protein needs without supplements.
2. What is the best time to consume protein?
Spread protein intake throughout the day. Include it in every meal to support metabolism, muscle repair, and satiety.
3. Which vegetarian protein is best for muscle building?
Paneer, tofu, lentils, and Greek yogurt are great muscle-building vegetarian proteins. Pair with strength training.
4. Are plant-based proteins complete?
Most aren’t, but combining different sources (like lentils and grains) gives a complete amino acid profile. Quinoa and soy are exceptions—they’re complete on their own.
5. Is protein only important for bodybuilders?
No. Protein is essential for everyone — from children to the elderly — for immunity, growth, metabolism, and healing.
🧠 Conclusion
Protein is much more than a bodybuilder’s nutrient. It’s a crucial macronutrient that supports every aspect of health — from your muscles and hormones to your immunity and skin. Vegetarians have a wide and colorful range of protein-rich foods that are as functional as they are flavorful. So fill your plate wisely, and let your food be your fuel!
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us