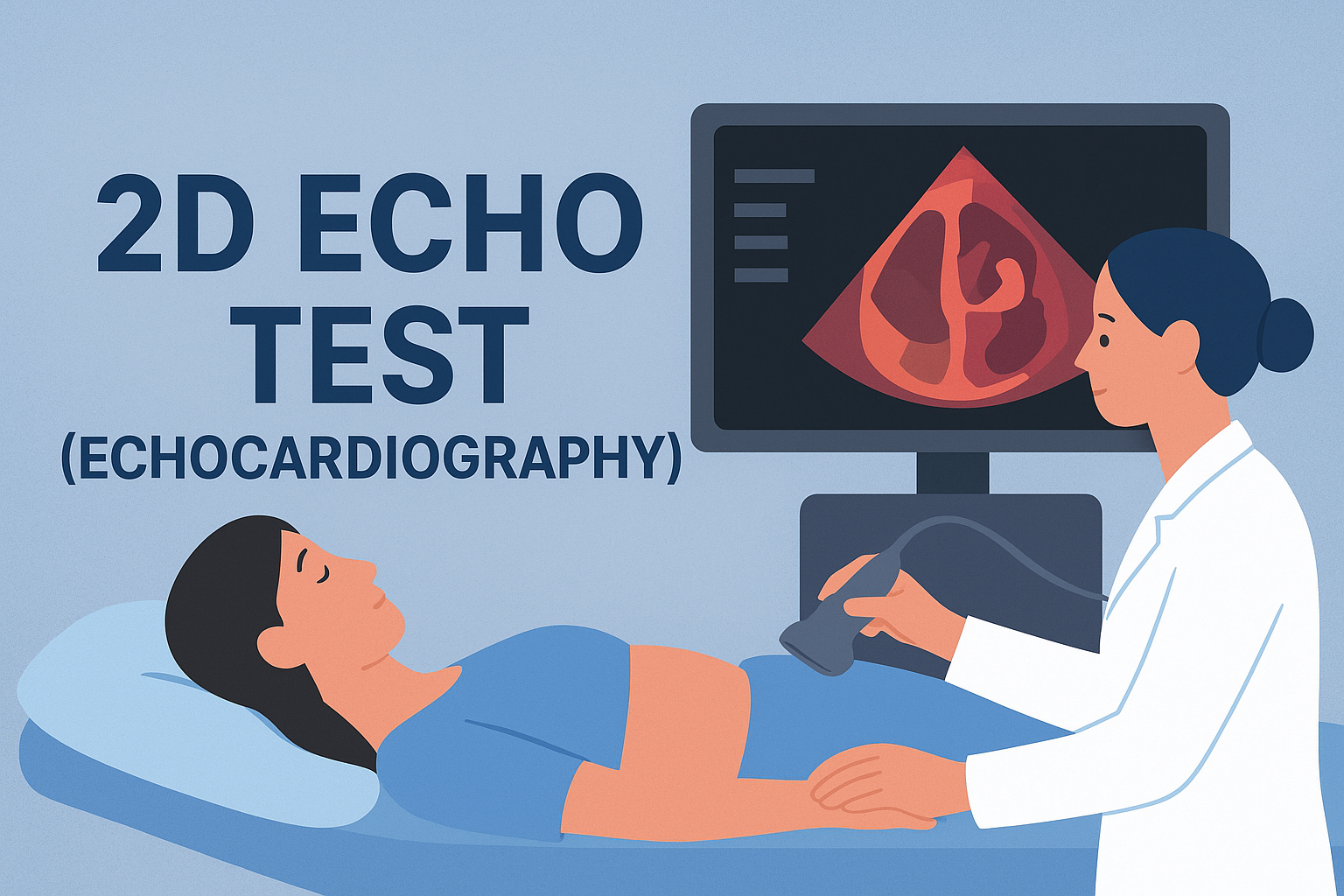
2D Echo Test (Echocardiography): Uses, Procedure, Normal Values, Cost, and Clinical Importance
Introduction
Heart diseases are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early diagnosis and timely monitoring play a crucial role in preventing serious cardiac complications. One of the most reliable, non-invasive, and widely used diagnostic tools for heart evaluation is the 2D Echo test, also known as Two-Dimensional Echocardiography.
A 2D Echo provides real-time images of the heart, helping doctors assess heart structure, pumping capacity, valve function, and blood flow. This test is commonly prescribed in patients with hypertension, diabetes, chest pain, breathlessness, heart murmurs, and post-heart attack follow-up.
This article explains what a 2D Echo is, how it works, its clinical uses, procedure, interpretation, normal values, risks, and cost, making it highly valuable for pharma and healthcare audiences.
What is a 2D Echo Test?
A 2D Echo (Two-Dimensional Echocardiography) is a non-invasive ultrasound test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create moving images of the heart.
It helps visualize:
- Heart chambers (atria and ventricles)
- Heart valves
- Heart wall thickness and movement
- Blood flow patterns
- Overall cardiac function
Unlike ECG, which records electrical activity, 2D Echo shows the actual structure and mechanical function of the heart.
How Does a 2D Echo Work?
The test uses a device called a transducer, which emits ultrasound waves. These waves bounce back after striking heart structures and are converted into real-time images on a monitor.
Key principles involved:
- Ultrasound reflection
- Doppler effect (for blood flow analysis)
- Real-time motion imaging
Types of Echocardiography
Although 2D Echo is the most common, it may be combined with other echo techniques:
1. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
- Most commonly performed
- Probe placed on chest wall
2. Doppler Echocardiography
- Assesses direction and speed of blood flow
- Detects valve stenosis or regurgitation
3. Color Doppler Echo
- Shows blood flow in different colors
- Useful in congenital and valvular heart diseases
4. Stress Echocardiography
- Done before and after exercise or medication
- Detects ischemic heart disease
Why is 2D Echo Test Done? (Indications)
Doctors recommend a 2D Echo for multiple clinical conditions, including:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Hypertension
- Diabetes with cardiac risk
- Heart murmurs
- Valvular heart disease
- Congenital heart defects
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart failure
- Post-myocardial infarction
- Pre-operative cardiac assessment
Clinical Importance of 2D Echo
2D Echo plays a vital role in:
- Early detection of heart diseases
- Monitoring disease progression
- Assessing treatment response
- Reducing unnecessary invasive procedures
- Guiding surgical and interventional decisions
For pharma professionals, 2D Echo is crucial in evaluating drug effects on cardiac function, especially in cardiotoxic medications.
Procedure of 2D Echo Test
The procedure is simple, painless, and safe.
Step-by-Step Process
- Patient lies on the examination table
- Gel is applied on the chest
- Transducer is moved over the chest area
- Images are recorded from different angles
- Test duration: 20–40 minutes
No anesthesia or injections are required.
Preparation for 2D Echo
- No fasting required (unless combined with stress echo)
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing
- Inform doctor about ongoing medications
- Remove chest accessories if any
Normal Values in 2D Echo
Some commonly assessed parameters include:
| Parameter | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| Ejection Fraction (EF) | 55–70% |
| Left Ventricular Size | Normal as per body size |
| Valve Motion | Smooth and normal |
| Wall Thickness | 6–11 mm |
| Blood Flow | Laminar |
⚠️ Values may vary depending on age, sex, and clinical condition.
Abnormal Findings in 2D Echo
A 2D Echo can detect:
- Reduced ejection fraction
- Valve stenosis or regurgitation
- Enlarged heart chambers
- Thickened heart walls
- Blood clots
- Congenital defects
- Pericardial effusion
Is 2D Echo Safe?
Yes. 2D Echo is extremely safe as it:
- Uses no radiation
- Is non-invasive
- Has no known side effects
- Can be repeated multiple times
It is safe for children, elderly patients, and pregnant women.
2D Echo vs ECG: Key Differences
| Feature | 2D Echo | ECG |
|---|---|---|
| Measures | Structure & function | Electrical activity |
| Imaging | Yes | No |
| Valve assessment | Yes | No |
| Radiation | No | No |
Both tests are complementary rather than alternatives.
Cost of 2D Echo in India
The cost may vary based on location and facility:
- Government hospitals: ₹800 – ₹1,500
- Private hospitals: ₹1,500 – ₹4,000
Advanced echo studies may cost more.
Role of 2D Echo in Preventive Cardiology
With rising cases of lifestyle diseases, 2D Echo is increasingly used for:
- Early detection in high-risk individuals
- Monitoring hypertensive and diabetic patients
- Preventing heart failure and sudden cardiac events
Conclusion
The 2D Echo test is a cornerstone of modern cardiology and preventive healthcare. Its ability to provide real-time, accurate, and detailed cardiac assessment makes it indispensable for clinicians, pharmacists, and patients alike.
For pharma websites, educating visitors about diagnostic tools like 2D Echo not only builds trust and credibility but also encourages early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is 2D Echo painful?
No, it is completely painless.
How long does the test take?
Usually 20–40 minutes.
Can 2D Echo detect heart blockage?
It can suggest reduced blood supply but angiography is needed for confirmation.
How often should 2D Echo be done?
As advised by the physician, especially in chronic heart conditions.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us