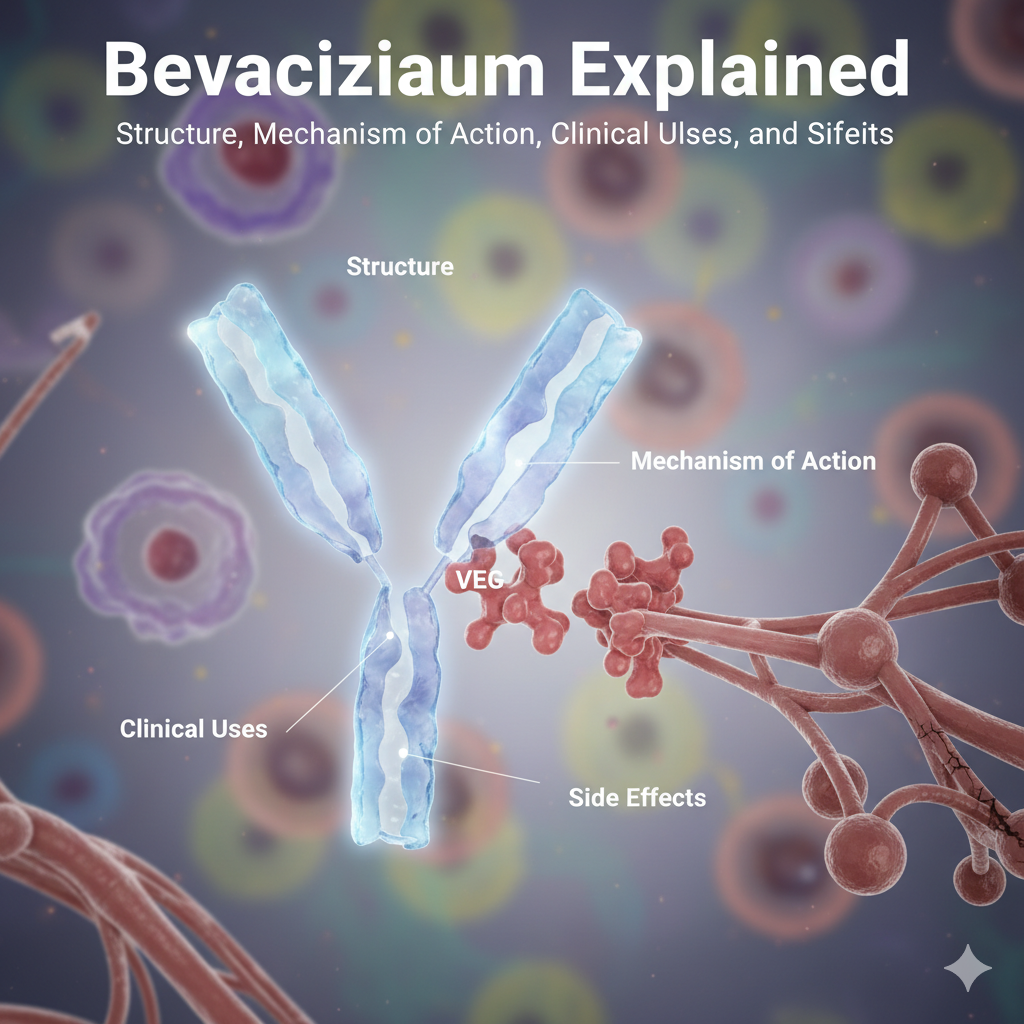
Bevacizumab Explained: Structure, Mechanism of Action, Clinical Uses, and Side Effects
Introduction
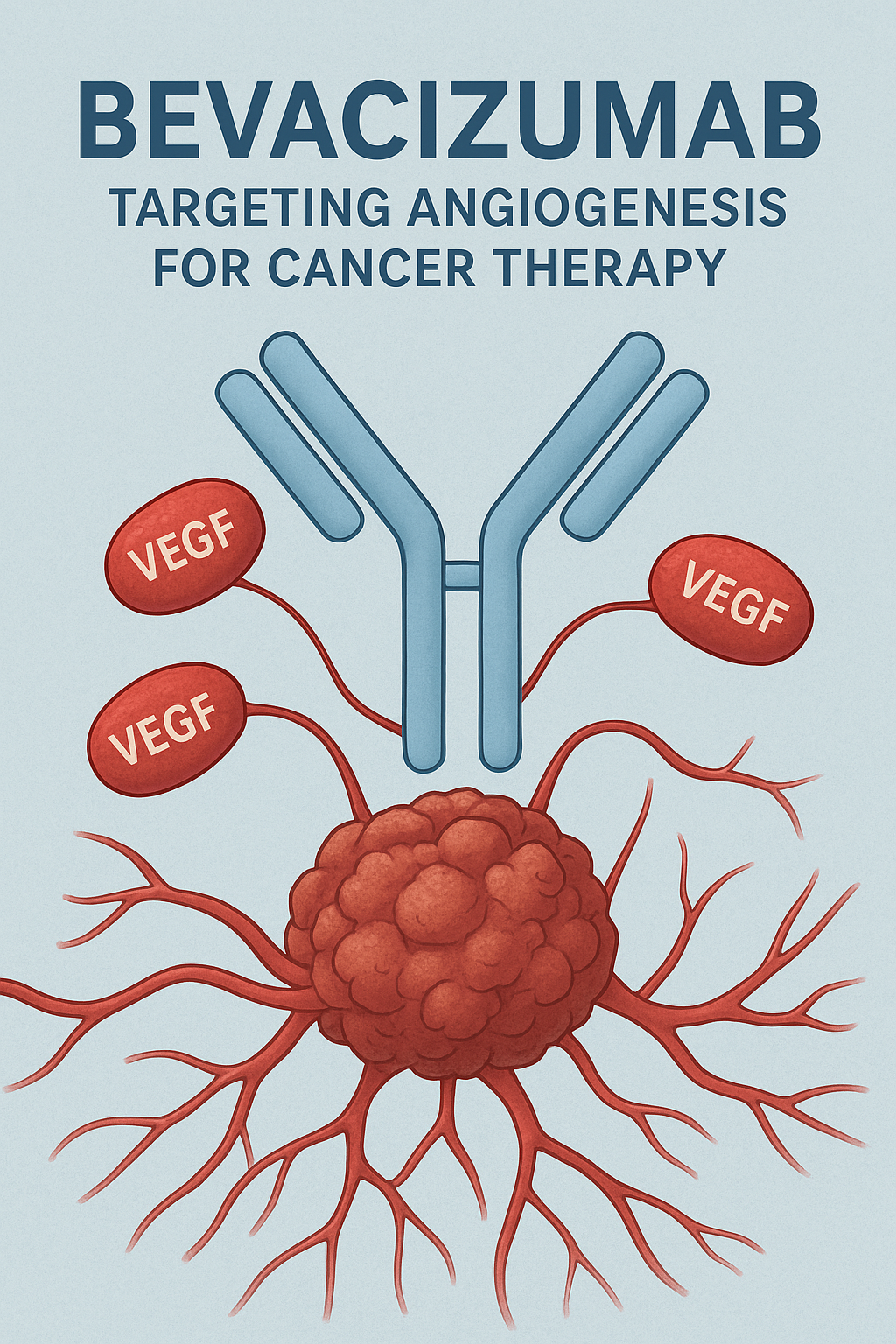
Bevacizumab, marketed primarily under the brand name Avastin®, is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). By blocking angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels—Bevacizumab effectively starves tumors of their blood supply, slowing their growth and metastasis.
Initially approved by the U.S. FDA in 2004 for metastatic colorectal cancer, Bevacizumab has since become a cornerstone in the treatment of several solid malignancies and ocular diseases characterized by abnormal neovascularization.
Structure of Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody produced using recombinant DNA technology in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells.
- Molecular Formula: C6638H10160N1720O2108S44
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 149 kDa
- Type: Recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody
- Target: VEGF-A (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A)
Structural Characteristics
- Composed of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains, typical of IgG1 antibodies.
- Human framework regions (~93%) with murine (mouse) complementarity-determining regions (~7%) to maintain specific VEGF binding.
- The Fab region binds to VEGF-A, while the Fc region interacts with immune effectors and provides stability and a longer half-life.
- It specifically recognizes and binds VEGF-A isoforms (VEGF121, VEGF165, etc.), preventing their interaction with VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 receptors on endothelial cells.
Medicinal Chemistry
Bevacizumab belongs to the biologic class of drugs, not small-molecule drugs. Hence, its chemistry involves protein engineering rather than synthetic organic chemistry.
- Type: Recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against VEGF-A.
- Source: Human (∼93%) and murine (∼7%) sequences.
- Production: Cultured in genetically modified mammalian (CHO) cells.
- Formulation: Lyophilized powder or solution for intravenous infusion; ophthalmic preparations are used off-label.
Stability and Storage
- Store between 2–8°C, protected from light.
- Do not freeze or shake.
- Dilution and handling require aseptic conditions to prevent protein denaturation.
Pharmacological Actions
Bevacizumab acts as an anti-angiogenic and antineoplastic agent.
Primary Pharmacological Actions
- Anti-angiogenic effect:
By binding VEGF-A, Bevacizumab prevents endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and survival—thereby inhibiting formation of new capillaries essential for tumor growth. - Anti-tumor effect:
Reduced blood vessel formation leads to decreased tumor perfusion, oxygenation, and nutrient supply, slowing tumor growth and metastasis. - Vascular normalization:
It transiently “normalizes” abnormal tumor vasculature, improving the delivery of chemotherapy agents and oxygenation during radiotherapy. - Reduction of vascular permeability:
It decreases vascular leakage, useful in conditions like macular edema and retinopathy.
Mechanism of Action (Detailed)
Normal VEGF Function
VEGF-A is a key mediator of angiogenesis. It binds to VEGF receptors (VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2) on the surface of endothelial cells, triggering:
- Proliferation and migration of endothelial cells
- Formation of new capillaries
- Increased vascular permeability
Mechanism of Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab binds and neutralizes VEGF-A, preventing its interaction with VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2.
This results in:
- Inhibition of angiogenesis (cutting off tumor blood supply)
- Reduced tumor vascular permeability
- Slower tumor progression
- Enhanced efficacy of cytotoxic chemotherapy due to improved vascular normalization
Thus, Bevacizumab effectively starves tumors and helps stabilize ocular neovascular diseases by limiting aberrant blood vessel formation.
Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Route of Administration | Intravenous infusion |
| Absorption | Not applicable (given IV) |
| Distribution | Volume of distribution ≈ 3 L; confined to plasma and interstitial fluid |
| Metabolism | Catabolized by proteolytic enzymes into small peptides and amino acids |
| Elimination Half-life | ~20 days (range: 11–50 days) |
| Excretion | Via reticuloendothelial system; not renally or hepatically cleared |
| Steady State | Reached after 100 days (approx. 4–5 doses) |
Clinical Uses
Bevacizumab has a broad range of oncologic and ophthalmic indications.
1. Oncologic Indications
a. Colorectal Cancer
- Use: In combination with fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer.
- Mechanism: Inhibits angiogenesis in tumor microenvironment.
b. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Use: First-line treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel in nonsquamous NSCLC.
c. Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Use: Combined with interferon alfa for metastatic RCC.
d. Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Use: For recurrent disease as monotherapy.
- Effect: Reduces tumor-associated edema and vascular permeability.
e. Ovarian and Cervical Cancer
- Use: In combination with paclitaxel and cisplatin or topotecan for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic disease.
2. Ophthalmologic Indications (Off-label)
Although not FDA-approved for ocular use, Bevacizumab is widely used off-label for:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Diabetic macular edema (DME)
- Retinal vein occlusion
- Neovascular glaucoma
In these conditions, VEGF overexpression leads to abnormal retinal neovascularization and leakage, causing vision loss.
Bevacizumab helps regress these vessels and reduce macular edema.
Dosage and Administration
General Principles
- Administer only as intravenous infusion (not IV bolus).
- Dilute in 0.9% sodium chloride.
- First infusion over 90 minutes, subsequent ones may be shortened if tolerated.
- Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Typical Doses
| Indication | Dosage (Adult) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Metastatic colorectal cancer | 5–10 mg/kg IV | Every 2 weeks |
| NSCLC (nonsquamous) | 15 mg/kg IV | Every 3 weeks |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 10 mg/kg IV | Every 2 weeks |
| Glioblastoma | 10 mg/kg IV | Every 2 weeks |
| Ovarian/Cervical cancer | 15 mg/kg IV | Every 3 weeks |
| Ophthalmic (off-label) | 1.25 mg/0.05 mL (intravitreal) | Every 4–6 weeks |
Adverse Effects
Common Side Effects
- Hypertension
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Proteinuria
- Epistaxis and minor bleeding
- Gastrointestinal upset
Serious Adverse Effects
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- Hemorrhage (including pulmonary or GI bleeding)
- Arterial thromboembolism (stroke, myocardial infarction)
- Delayed wound healing
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
- Nephrotic syndrome (due to glomerular microangiopathy)
Ophthalmic Use Complications
- Endophthalmitis
- Retinal detachment
- Intraocular inflammation
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to Bevacizumab or any component of the formulation.
- Pregnancy (Category C – potential teratogenicity due to VEGF inhibition).
- Recent surgery or open wounds (impaired wound healing).
- Active bleeding or severe hemorrhage risk.
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
Precautions and Warnings
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Avoid; may cause fetal harm.
- Surgery: Withhold at least 28 days before and after surgery.
- Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure regularly.
- Proteinuria: Regular urine protein checks required.
- Cardiac toxicity: Caution with prior anthracycline therapy.
Drug Interactions
- No major CYP450-mediated interactions.
- Additive toxicity possible with:
- Cytotoxic chemotherapy (increased risk of bleeding and perforation)
- Antiplatelets/anticoagulants (risk of hemorrhage)
- Radiotherapy (delayed wound healing)
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
Bevacizumab’s efficacy has been demonstrated in several landmark trials:
| Trial | Cancer Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| AVF2107g | Colorectal cancer | Improved median survival by ~4.7 months with Bevacizumab + FOLFOX |
| E4599 | NSCLC | Significant improvement in overall survival |
| AVAglio | Glioblastoma | Prolonged progression-free survival |
Pharmacovigilance and Monitoring
Parameters to monitor:
- Blood pressure (before each dose)
- Urine protein (dipstick or 24-hour protein)
- Signs of bleeding or perforation
- Neurological symptoms (for RPLS)
- Wound healing status
Biosimilars
Several Bevacizumab biosimilars are now available globally, enhancing accessibility:
- Mvasi® (Amgen)
- Zirabev® (Pfizer)
- Abevmy® (Biocon/Viatris)
- Bevacirel®, Bevatas® (India)
These are approved based on equivalence in efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity compared to the reference product.
Conclusion
Bevacizumab remains a landmark in targeted cancer therapy, offering survival benefits across multiple malignancies through VEGF inhibition. Its evolving role in ophthalmology further emphasizes the therapeutic potential of anti-angiogenic strategies.
However, the drug demands careful patient selection and vigilant monitoring due to risks of hypertension, bleeding, and wound healing complications.
As biosimilars emerge, the accessibility of this life-saving biologic continues to expand globally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary mechanism of action of Bevacizumab?
Bevacizumab binds to VEGF-A, preventing it from activating VEGF receptors on endothelial cells. This inhibits angiogenesis, cutting off the tumor’s blood supply.
2. Can Bevacizumab be used for eye disorders?
Yes. Although not officially approved for ophthalmic use, it is widely used off-label for age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema.
3. What are the main side effects of Bevacizumab?
Common side effects include hypertension, proteinuria, fatigue, and bleeding. Serious risks include GI perforation, thromboembolic events, and impaired wound healing.
4. Why should Bevacizumab be avoided before surgery?
Because it inhibits new blood vessel formation, it can impair wound healing. Hence, it should be withheld at least 4 weeks before and after surgery.
5. Are Bevacizumab biosimilars as effective as the original Avastin?
Yes. Approved biosimilars such as Mvasi® and Zirabev® have demonstrated comparable efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetic profiles.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us